
MSBA Capstone Corporate Sponsorship
MSBA Capstone Corporate Sponsorship
Capstones are immersive, experiential courses that culminate a graduate program experience. Industry partners are an integral part of making these courses impactful learning experiences for students.
Your company provides the business challenge. Tepper MSBA students apply their deep analytical skills, business knowledge, and creative problem-solving expertise to transform data into better decision-making and a competitive advantage for your business.
Our MSBA students are equipped with leading-edge knowledge, skills, and experiential training, including:
- Methodology, including machine learning and optimization.
- Software Engineering including large-scale data management and programming in R and Python.
- Corporate Communication, including communicating with non-technical stakeholders.
- Business Domain Knowledge including marketing, operations, accounting, finance, and people analytics.
Contact Jen Cadman, Director of Corporate & Foundation Relations, to find out more about sponsoring a capstone course.
Recent MSBA Capstones
 Busy Beaver: Increasing Transaction Size Through Data Analytics
Busy Beaver: Increasing Transaction Size Through Data Analytics
Capstone Team: Christian Meyer, Haider Aly Reza, Nico Roussel, Paul Lim
How can a traditional retailer motivate customers to increase their basket size? The answer to this question may be hiding in Busy Beaver’s database of historical customer transactions. Included in this vast dataset is information about how customers responded to prior promotional campaigns, which primarily take the form of biweekly advertisements that promote various discounted products. The key question is how effective these promotions are at driving incremental business. Moreover, are there opportunities for improvement by adjusting product selection and/or discount levels? Finally, how should seasonality influence the design of the promotions?
The approach chosen to address these questions was to apply modern machine learning techniques to understand the relationship between the various characteristics of a promotion and their corresponding impact on customer purchase behaviors. This approach enabled the identification of key insights that will likely improve management’s ability to design their biweekly advertisements. Ultimately, these insights formed the basis for a proof-of-concept application that illustrates how advanced data analytics can be used to help improve the effectiveness of key business decisions and for future work to continue to understand the donor base behavior, especially as more data becomes available.
Capstone Presentation
 CMU Giving: Unlocking Generosity With Analytics
CMU Giving: Unlocking Generosity With Analytics
Capstone Team: Roopa Bharadwaj, Yang Liu, Mark Denton
Growing a sustainable giving program is a key strategy for CMU. But finding and converting these donors to be regular or upgrade their donations isn’t easy.
CMU has been growing the donation base of alumni that participate in annual giving, volunteering, or other events. Appeals are a cornerstone for fundraising programs. But running them inefficiently by targeting the wrong alumni with wrong ask amounts is often a pain point.
Capstone Presentation
 Emerson: Greenhouse Gas Reduction Program
Emerson: Greenhouse Gas Reduction Program
Capstone Team: Will Chastka, Yuhan Chen, Hema Kadali, Alexis Robbins, Zelealem Yima
As part of Emerson’s Environmental Sustainability journey, Emerson is looking for accurate and innovative approaches to calculate CO2emissions and identify opportunities to achieve their Net Zero objectives. MSBA students analyzed their data, conducted market research and developed newer methods and Machine Learning models for emission predictions. We also built data stories and what-if scenarios to demonstrate the ‘art of possible’.
Capstone Presentation
 Glance: Improving Click-through Rate on Mobile Lock Screen Advertisements
Glance: Improving Click-through Rate on Mobile Lock Screen Advertisements
Capstone Team: Hugo Camou, Johnathan Khodr, Jamie Khoo, Andrew Lee
Glance delivers its users interactive content (cards) to their phone’s lock screens. “Clicks” on sponsored cards is a measure of success for a campaign. Dividing clicks by the number of impressions gives click-through rate (CTR), a key metric when comparing success across campaigns.
Glance already utilizes a sophisticated recommendation system to distribute cards to its users. (Oli et al., 2020) However, to maximize revenue, it is important to understand what motivates a user to interact with a sponsored card. Thus, our goal was to create a modeling methodology that improves upon the existing recommendation system, makes consistent predictions across multiple card types, and offers interpretable results.
By predicting clicks on a target glance at a user level, we were able to develop a modeling methodology that achieves each of these goals. We feature engineered user data and past click history to make our predictions and found that past click history was most predictive of future clicks.
Capstone Presentation
 Honda: 99PLabs Research - Dynamic Vehicle Services
Honda: 99PLabs Research - Dynamic Vehicle Services
Capstone Team: Chatchawan Lakkhananukun, Prakhyat Pola, Rebecca Stevens, Jocelyn Wang
In this project, we explored two business models: a car maintenance service and a peer-to-peer car lending platform; we used an analytics-focused approach on the Telematics dataset collected on cars provided by 99PLabs. Dwell time and location predictive models were developed previously by another team, and we provided recommendations on the model improvement.
The two business models integrate the predictive models to create potential business values. Because of the limitation of the dataset, two surveys were conducted to understand and validate our business models. Both surveys showed that there are markets for the two proposed business models. We also developed a framework to understand the failure modes of both business models and methods for mitigating the risk. We analyzed the cost-benefit of applying the predictive models to both business models to understand potential values for both 99PLabs and its customers. Finally, we explored the potential of using autonomous vehicles in the peer-to-peer lending service.
Blog: Leveraging Dwell Time Models to Create Dynamic Vehicle Services (Peer-to-Peer Car Lending Service)
Capstone Presentation
 Industrial Scientific: Customer Insights
Industrial Scientific: Customer Insights
Capstone Team: Ralph Del Negro, Milica Kosic, Rohi Nallamolu, Alexandra Quan, Amy Ran
The sponsor company has noticed an opportunity to improves upsell and cross-sell activity by using historical data to identify which sites are using less product than they need. The Tepper MSBA team met with members of the marketing, sales, field services, and IT teams to understand the business and data context. These interviews identified the key problem of understanding how account characteristics and behavior impact downsells and upsells.
Using product data, Salesforce account information, and contract amendment data, the Tepper team prototyped multiple machine learning models to predict product utilization rates, contract changes, and equipment volume. Ultimately the team refined a customer segmentation model, which used k-means clustering on the principal components of an 80 feature dataset.
The customer segmentation model output 3 clusters: low risk of downsells, moderate risk of downsells, and high growth opportunities. Key insights of these models include strong correlation between customer activity and upsells, the importance of product choice in predicting contract amendments, and the observable predictive value of the company’s own customer health metric.
Capstone Presentation
 Reducing Tier 2 Creator Churn on Roposo Through Targeted Intervention, Sponsored by InMobi
Reducing Tier 2 Creator Churn on Roposo Through Targeted Intervention, Sponsored by InMobi
Team Members: Sagar Dubey, Emma MacKay, Dipali Mistri and Sruthi Suresh
Roposo, a short video-sharing platform owned by InMobi, is challenged by the severe lack of “active” creators, causing less diverse content creation. The dormant or “Tier 2” creators far outnumber the most active “Tier 1” creators. Roposo is looking to identify levers to encourage less active creators to create more content leading to higher creator and content diversity. This would also reduce the concentration of views toward popular creators in the Roposo ecosystem.
Our purpose was to identify Tier 2 creators and find levers that could incentivize them into posting more often, or in other words, reduce their churn. We ran k-means clustering on the set of creators and found that there are five distinct clusters, among which two lie on each extreme – most active (Tier 1) and totally inactive. Our focus then was on the three remaining Tier 2 clusters. During EDA, we found that views and posting frequency were correlated, and so hypothesized giving additional views as a potential lever. We ran survival analysis on the three clusters separately to define a churn cut-off for each, accounting for when 90% of creators in each cluster had posted. We used a combination of survival analysis, decision tree, and poisson regression models to propose that InMobi offer free views to those creators from the three Tier 2 clusters, who have less than 750 average views in the past 14 days. Doing so would potentially cause these creators to post more often, and not churn as a result.
Download the Presentation (PDF)
Introduction
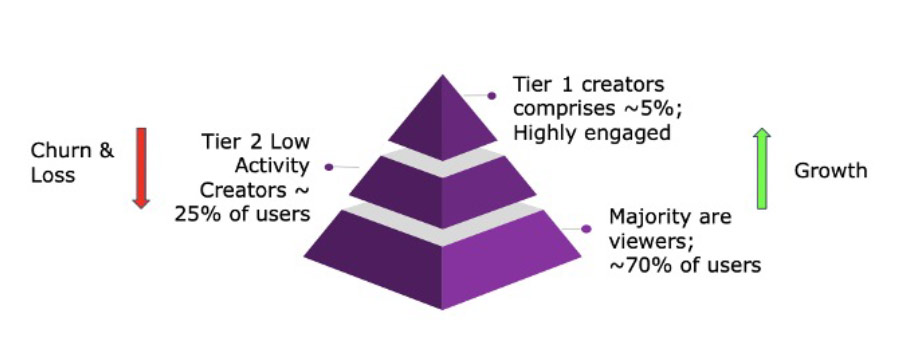
Roposo, owned by InMobi, is an Indian “short” video (shorter than 3 minutes) creation and sharing app, available in various local languages. Users on Roposo create short videos on its various channels dedicated to comedy, religion, dance, food, health, movies among others. A small subset of creators on the platform thrive (Tier 1) with the remainder lagging behind and having high churn rates (Tier 2). The remainder of users on the platform are viewers (Figure 1).
In this project, our ultimate goal is to decrease the churn rate of Tier 2 creators by addressing the following questions: Who is likely to churn and why? If possible, can we determine the optimal intervention strategies to reduce the likelihood of churning?
Methods and Materials
Our analysis is focused on a subset of creators from the months of September 2020 to January 2021. Our dataset includes various characteristics about the creators, including demographic, behavioral, and engagement features.
We transform our data into time-series features. Specifically, we look at 1, 7, 14, 30, and 60-day rolling windows and compute metrics such as the number of views, the count of videos, and the average inter-posting time. We furthermore record demographic features such as gender, age, and tenure. At this stage, we also compute our target variable, which is the time to the next video posting and the count of videos posted.
Results
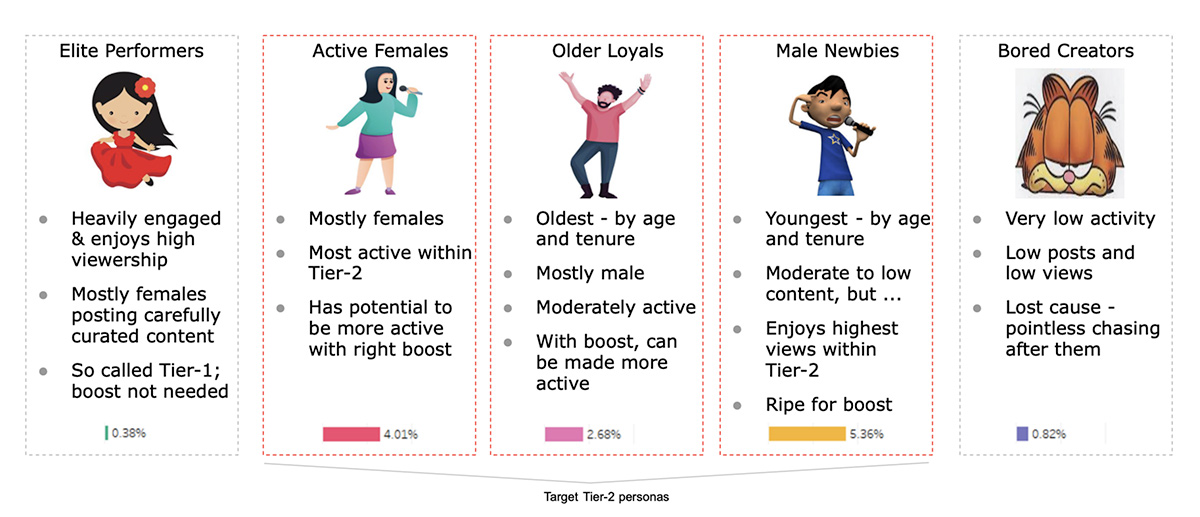
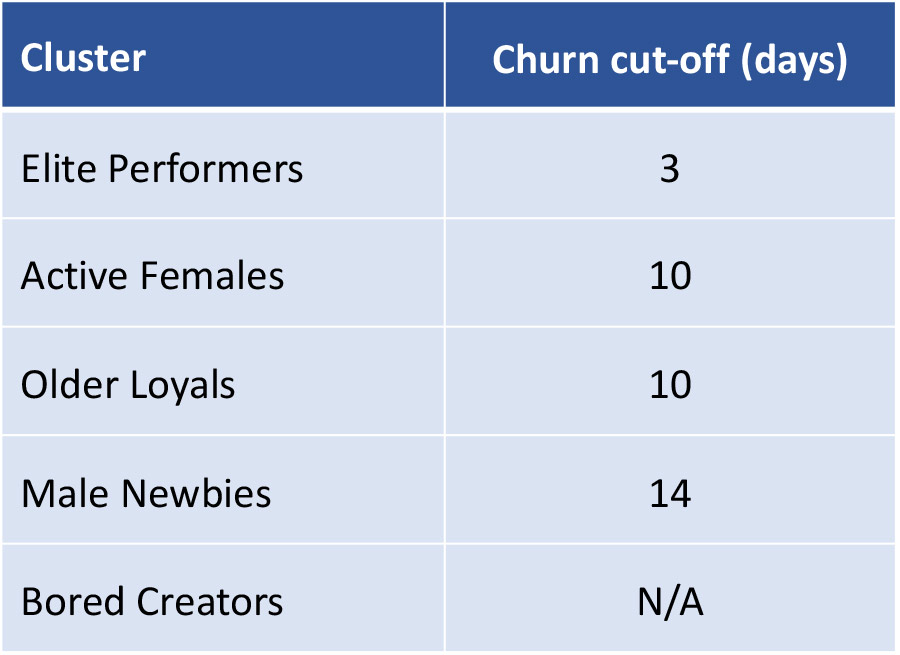
We distinguish Tier 1 and Tier 2 creator characteristics through K-means clustering. As shown in Figure 2, the Elite Performers do not need further incentives and generally have low churn, whereas the Bored Creators may not respond to any kind of intervention given their low activity on the platform. Therefore, our recommended intervention strategy focuses on Older Loyals, Male Newbies, and Active Females. Survival analysis further highlights the difference in posting characteristics (Figure 3). We also use this to define churn as the number of days where 90% of creators are expected to post since their last video.

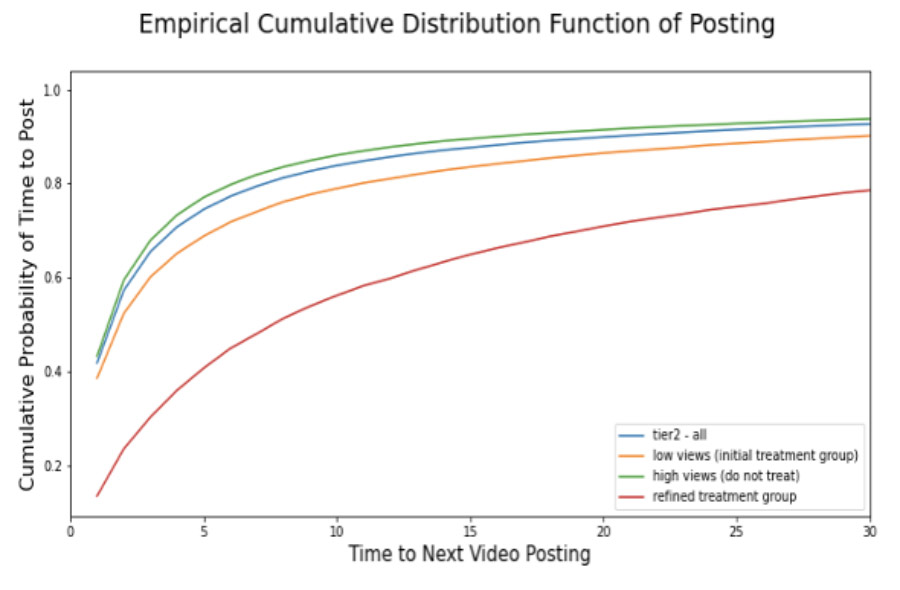
We find that views are highly concentrated on the platform, and that within our target Tier 2 personas, those with lower views post less frequently. Based on these findings, we initially propose a strategy to boost views for Tier 2 creators who have less than 750 views in the preceding two weeks. We further refine this target group based on a creator’s behavioral characteristics (count of videos posted and time since last video) and find that those within our refined target group are at much greater risk of churn (Figure 4).
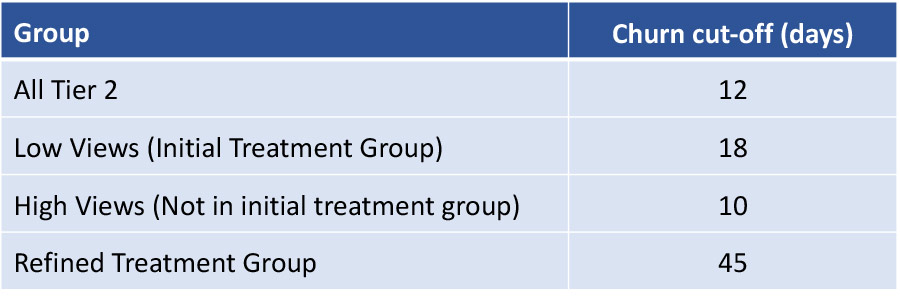
Discussion
Based on earlier analysis, we observe that the ideal group to target for increased views are Tier 2 creators who had less than or equal to 750 average views in the past 14 days. We attempt to further refine this target group using a tree-based classification model. The results from this model suggest refining our treatment group based on the number of videos a creator has posted in the past 14 days and days since last video posting.
We re-run our survival models to observe the posting characteristics of our proposed treatment group and compare the results to our previous proposed treatment group that was defined based on views. We find that the refined target group has significantly longer inter-posting times than the remaining members of their persona as well as those targeted solely based on views. This suggests that InMobi can better ration “free” boosted views to those most at risk. We furthermore confirm that Older Loyals and Male Newbies appear to be more sensitive to the number of views, meaning that increased views are predicted to have greater impact for Older Loyals and Male Newbies than for Active Females. As mentioned above, this provides a further way for InMobi to prioritize free views.
Conclusions
To conclude, we note a few key highlights that we uncovered during this project. Views and posting frequency are correlated, and a few top creators, namely the Tier 1 creators, capture a high percentage of total views on the platform. The remaining creators, that is, Tier 2 creators, differ by their posting characteristics, and by extension, views, and clustering allows us to better understand the various personas that exist among Tier 2 creators.
Tier 2 creators suffer from churn, but given that creator churn is non-contractual or deterministic, we loosely define churn based on posting characteristics within each persona. There are several ways that InMobi can help less successful creators on the platform, including artificially boosting views, which is expected to reduce inter-posting time. While less successful creators can be broadly targeted, targeting specific creators based on behavioral and demographic rules will allow for a greater impact.
 LISI: Implementing a Newsletter Recommendation System: How Leimberg Services Inc. Can Improve Customer Satisfaction
LISI: Implementing a Newsletter Recommendation System: How Leimberg Services Inc. Can Improve Customer Satisfaction
Capstone Team: Cyndia Chen, Olivia Dion, Jackie Sun, Haowei Song, Yifei Wang
This paper explores the implementation of a newsletter recommendation system for Leimberg Services Inc. (LISI) to enhance customer satisfaction. The research leverages machine learning algorithms and data analysis to segment subscribers and predict their newsletter interests. By collecting demographic information and consumption records, along with newsletter content, the study identifies clusters of subscribers and matches them with relevant newsletters based on keyword similarity. The findings provide valuable insights for LISI to personalize email marketing campaigns, improve customer segmentation, and conduct A/B testing for optimization. The proposed strategies encompass recommendation systems, customer segmentation, and A/B testing, which can contribute to increased subscriber engagement, retention, and revenue. Additionally, suggestions are given for future improvements, including adjusting the registration system, providing clearer categorization options, and establishing a comprehensive database with interactive data collection. These recommendations aim to enhance personalization, improve user experience, and enable data-driven decision-making to optimize LISI's service and content over time.
Capstone Presentation
LISI: Strategic Vision and Business Plan For Leimberg Information Services' Growth
Capstone Team: Alicia Carter, Erin Murphy, Deanna Swinerton, Tiffany Wang, Daniel Weiss
Leimberg Information Services, or LISI, is a niche content provider for Estate and Tax attorneys, CPAs, and financial professionals and companies. LISI offers newsletters, webinars, podcasts, courses, and other content to its customers. Historically, LISI has been run like a hobby. It is now under new ownership, and they want to expand profitably and sustainably. Due to poor data collection, and no real organizational structure, they didn't know where to start.
Overview of Solutions:
Tepper MSBA students proposed three methods to drive LISI's growth:
- Develop an extensive podcast platform.
- Expand the reach of their newly created product The Institute.
- Build a networking platform based on the expertise of LISI's subscribers.
Capstone Presentation
 PGT Trucking Order Selection Project
PGT Trucking Order Selection Project
Capstone Team: Jiarui Wang, Jiadi Zhang, Peter Pan, Sanjit Sokhi, Zhiyu Pan
PGT Trucking faces a high surplus of demand. It receives far more order requests for hauling services than it could satisfy. Therefore, PGT requires an automated algorithm that helps it selectively accept the optimal combination of order requests that not only produce high revenue but do not conflict with each other geographically or time-wise.
Capstone Presentation
 Synechron: Improving Employee Retirement Experience with Actionable Financial Wellness Programs
Synechron: Improving Employee Retirement Experience with Actionable Financial Wellness Programs
Capstone Team: Aishwarya Shah, Ryannon Starkey, Gnanitha Manne, Mindaugas Katilius, Evan Wong
There are three major concerns in the retirement industry:
- Very few people are focused on saving for retirement.
- People may need to take money out early for emergencies which reduces retirement corpus.
- More money is being spent on services and products impacted by inflation.
One-third of Americans feel unprepared or unsure of whether they are on track for retirement, one of the main reasons being the lack of engagement between employers/plan providers and employees. The purpose of this study is to examine these challenges and provide insights into the ways that employers and plan providers could help improve the contribution rate.
Capstone Presentation
 Parcel Consolidation in Last-Mile Delivery, Sponsored by Tata Consultancy Services
Parcel Consolidation in Last-Mile Delivery, Sponsored by Tata Consultancy Services
Team Members: Kristina Schiffhauer, Sivanagahari Devarapalli, Stefanie Montgomery, and Timothy Marshall
Parcel delivery companies (i.e., United Parcel Service, FedEx, Amazon) are challenged with an intricately complex logistical problem - moving parcels from origin to destination as efficiently as possible. The final leg of delivery logistics is last-mile delivery. For customers with relatively frequent orders, multiple parcels are likely to pass through the same last mile over a short time frame.
We explore an approach to achieve cost savings through the implementation of a parcel consolidation program. We introduce a framework to target the most valuable customers and compare customer-facing incentives to motivate program participation.
Our experiments have shown that parcel consolidation schemes are an effective way to reduce last-mile costs. Specifically, given enough capacity to store held parcels overnight at the last-mile hub, the marginal stop costs saved outweigh the parcel storage costs. Dynamic parcel consolidation has the highest savings, but is not feasible to implement in real-life.
Two days per week assigned delivery days has higher savings compared to single day of week assigned delivery, due to the fact that more destinations can be included in the program under the two days per week delivery scheme.
Last-Mile Delivery Is Critical
 The last-mile delivery cost function is complicated and depends on many parameters such as transportation hub's fixed and variable costs of truck, fuel, distance traveled, time duration, parcel weight, and volume. Due to confidentiality and a competitive market, major parcel carriers’ actual last-mile delivery cost function is not available publicly. Gevaers, et al. (2014) modeled total last-mile costs by modeling specific last-mile characteristics as independent variables.
The last-mile delivery cost function is complicated and depends on many parameters such as transportation hub's fixed and variable costs of truck, fuel, distance traveled, time duration, parcel weight, and volume. Due to confidentiality and a competitive market, major parcel carriers’ actual last-mile delivery cost function is not available publicly. Gevaers, et al. (2014) modeled total last-mile costs by modeling specific last-mile characteristics as independent variables.
In our simplified version, we have referenced two sources to derive cost per delivery stop from quarterly earnings reports of parcel carriers (UPS and FedEx) and the annual ATRI (American Transportation Research Institute) report provides transportation cost per hour and transportation cost per mile. These studies suggest an average last-mile delivery cost per stop of about $4.50, which is the number we use in our optimization model.
 Key Questions/Hypothesis
Key Questions/Hypothesis
- Parcel consolidation beyond promised delivery date reduces last-mile delivery costs.
- There are incentives that motivate customers to opt-in for delayed parcel delivery.
tcs-2.jpg
Framework Architecture
 We set forth a dual-workstream framework to evaluate our hypotheses. Workstream 1 aims to identify customers (destinations) to target for participation in consolidation programs. Workstream 2 aims to identify effective incentives for convincing customers to opt-in for participation in consolidation programs.
We set forth a dual-workstream framework to evaluate our hypotheses. Workstream 1 aims to identify customers (destinations) to target for participation in consolidation programs. Workstream 2 aims to identify effective incentives for convincing customers to opt-in for participation in consolidation programs.
In the diagram, we highlight the framework components that make up each workstream. Together, Workstream 1 and Workstream 2 form a framework that may be repeatedly employed by a parcel carrier to model and evaluate different real-world scenarios. By identifying the customers to target, and identifying what incentives are most effective, a parcel carrier may develop a strong consolidation program that will result in optimal operations savings.
Parcel Consolidation Does Improve Cost Savings
 A key component of our analysis is the mixed integer linear programming model built and solved using the DOCPLEX solver. The optimization model simulates the impact of our various consolidation strategies, with the primary benefit of identifying the destinations to target for consolidation which save the most costs, subject to our various constraints.
A key component of our analysis is the mixed integer linear programming model built and solved using the DOCPLEX solver. The optimization model simulates the impact of our various consolidation strategies, with the primary benefit of identifying the destinations to target for consolidation which save the most costs, subject to our various constraints.
Our experiments have shown that parcel consolidation schemes are an effective way to reduce last-mile costs. Specifically, given enough capacity to store held parcels overnight at the last-mile hub, the marginal stop costs saved outweigh the parcel storage costs. Dynamic parcel consolidation has the highest savings, but is not feasible to implement in real-life. Two days per week assigned delivery days has higher savings compared to single day of week assigned delivery, due to the fact that more destinations can be included in the program under the two days per week delivery scheme.
Survey Respondents Preferred Gift Card
 Incentive surveys reveal that parcel consolidation programs are viewed favorably by consumers. Roughly two-thirds of respondents indicated that they would participate in the two days per week fixed delivery model for no monetary incentive at all, though different monetary incentives increase the reported participation rate. Consumers prefer the two fixed days per week scheme over the dynamic scheme.
Incentive surveys reveal that parcel consolidation programs are viewed favorably by consumers. Roughly two-thirds of respondents indicated that they would participate in the two days per week fixed delivery model for no monetary incentive at all, though different monetary incentives increase the reported participation rate. Consumers prefer the two fixed days per week scheme over the dynamic scheme.
Given the willingness to participate in a consolidation program and the potential for cost savings, we recommend that parcel carriers implement a consolidation pilot program at key last-mile hubs without offering incentives for participation. In preparation for a pilot program, the framework described in this report can be applied to a real-last mile hub to reveal the optimal consolidation scheme, expected cost savings, and willingness to enroll in the program.
Vitalant: Blood Donation Donor Analysis
Capstone Team: Matt Greenfield, Sam Hartman, Josh Kennedy
Vitalant, the nation’s largest independent and nonprofit blood services provider, has been facing declining blood donations over the past decade. The United States as a whole is facing blood supply shortage.
Pittsburgh area donor information for a 12-year period was the basis of examination, analyzing, and modeling for the team. Data was taken through many iterations of analyzing trends and developing churn prediction models.
The team confirmed a handful of the theories posited by the Vitalant team sponsors and brought new information to light. The disparity among older and younger donors was confirmed, yet the team was able to identify that this is mainly due to lack of returning donors in younger generations. Donors that returned acted similarly across all generations.
The team was able to isolate which factors are indicative of higher churn (or lower retention), which are mainly the amount of prior visits and whether the previous visit was successful. While the team was able to confirm many suspicious and bring new trends to light, many of these analyses can be continued for future work to continue to understand the donor base behavior, especially as more data becomes available.
Capstone Presentation
Accounting for Seasonal and COVID in CLV Model Predictions for a Retail Chain
Capstone Team: Andrea Levy, Michael Zakin, Vivek Jayaprakasan
Customer Lifetime Value (“CLV”) modeling focuses on measuring and understanding the value of a customer based on past customer transaction data. Reliable models that accurately predict CLV is a critical tool that helps a company understand customer purchasing behavior, enabling managers to make focused marketing decisions.
Two common “buy-’til-you-die” probability models are used to predict CLV in non-contractual customer retail environments: the Pareto-NBD model (Reference 1), and the BG-NBD (Reference 2) model. One of the primary benefits of these types of models is that they work with aggregate data and are easy to implement.
Capstone Presentation
Is a CMU Capstone Sponsorship Right for Your Company?
For companies with unique problems, capstones offer a fast and low-cost path to a dedicated team of students who will offer fresh insight. At the same time, it is often challenging to identify when a capstone is appropriate and navigate the breadth of options available at CMU.
To that end, this session is a crash course on capstones at CMU, from ENAiBLE: A CMU Retail & Services Collaborative.