Accessibility
Web accessibility ensures that all people can understand and interact with your website. Carnegie Mellon University websites should provide equal opportunity to people with disabilities, according to the guidelines set forth by the World Wide Web Consortium's Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.1 standards.
The guidelines are categorized into three levels of compliance:
- A - must support
- AA - should support
- AAA - optional support
At a minimum, CMU websites should maintain Level AA compliance.
The WCAG quick reference guide provides examples and practical solutions to making your site Level AA compliant (note that Level AA compliance includes Level A compliance). You can also test your website with WebAIM's Web Accessibility Tool.
As a great starting point, adhere to the advice on this page, and hold your colleagues accountable by promoting accessibility and sharing this page.
Text
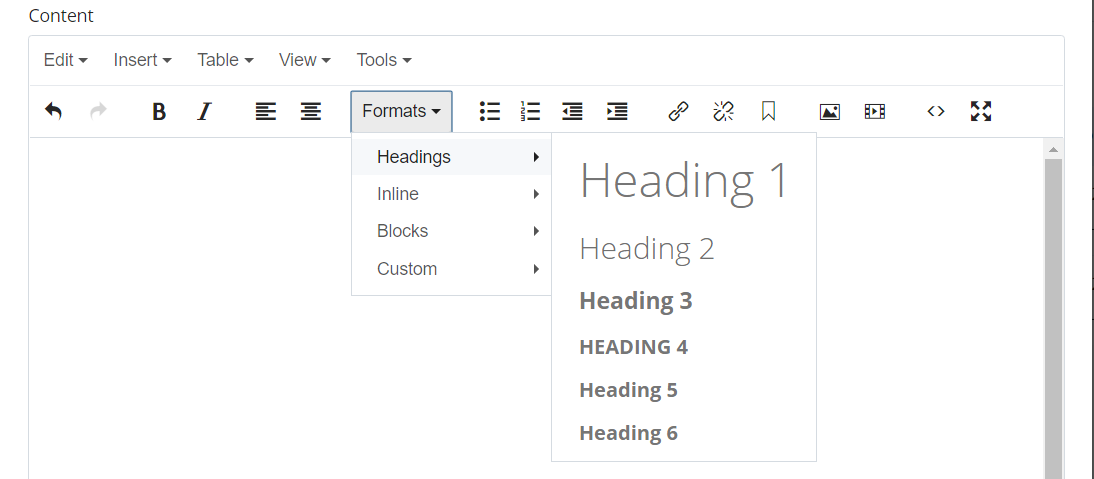
Structure your page using heading tags.
Heading tags establish contextual hierarchy and ensure that screen readers and search engines can understand your content. In the CMS, heading tags are in a drop-down menu.
Link relevant text.
Always use relevant text when creating links. Do not link generic words like "click here," "visit this page" and "read more."
Good
Visit Carnegie Mellon University's website.
Bad
To visit Carnegie Mellon University's website, click here.
Make accessible forms and documents.
Ensure that your PDF and Word Docs are accessible. Structure your content with headings and add alternative text to images. When creating forms, label every field and button, and group related fields with a fieldset and legend.
Avoid center-aligned text.
Large chunks of center-aligned text are difficult to read and can frustrate people who have reading disorders.
Use simple words.
If your page is meant for a general audience, consider using common words and short sentences. Limit adverbs, refrain from the passive voice and be aware of readability grade level.
Images
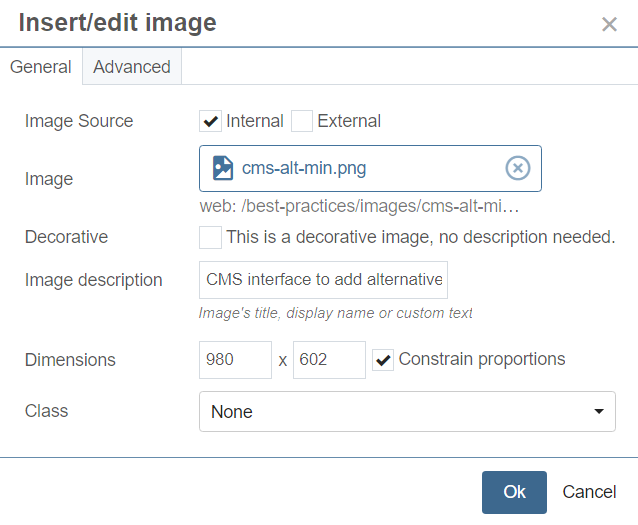
Add relevant alternative text to images.
People with vision impairment may not be able to see your images, so provide alternative text (alt text) for every image on your site. Alt text should describe an image to a person as if they couldn't see it.
- "Professor assists students in lab"
- "Students walking through Cohon University Center"
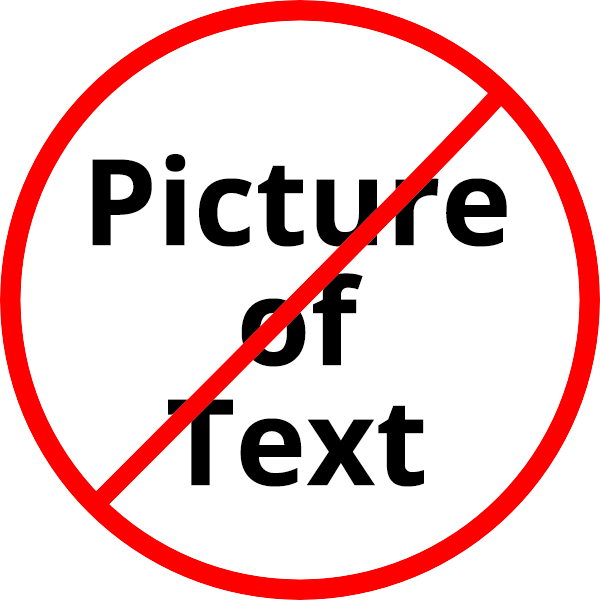
Don't use pictures of text.
Screen readers can't read text within an image. Please type text directly on the page. If you must use a picture of text, type the text in its alt attribute.
Embedded Content & Multimedia
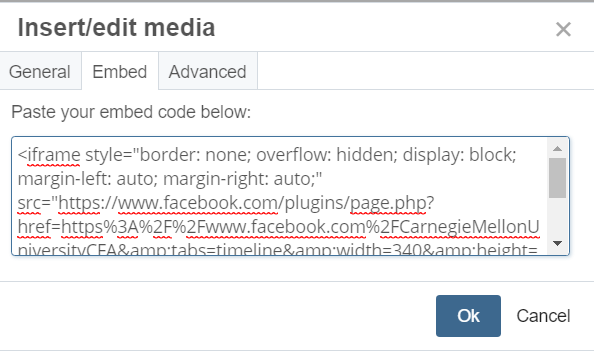
Widgets must be accessible.
If embedded content, such as an X widget, contains critical information, be sure that it is also accessible.
Videos must be accessible.
Use descriptive titles and captions for your videos. If your video contains critical information, provide a transcript too.