Robotics Competition Micro-credentials that lead to Industry-aligned Certifications
ARM Micro-Certifications (M-C) and Certifications
SMART integrates a set of industry-recognized certifications into the robotics competition ecosystem with the goal to foreground and measure the technical skills that ARM industry members seek in their technical employees.
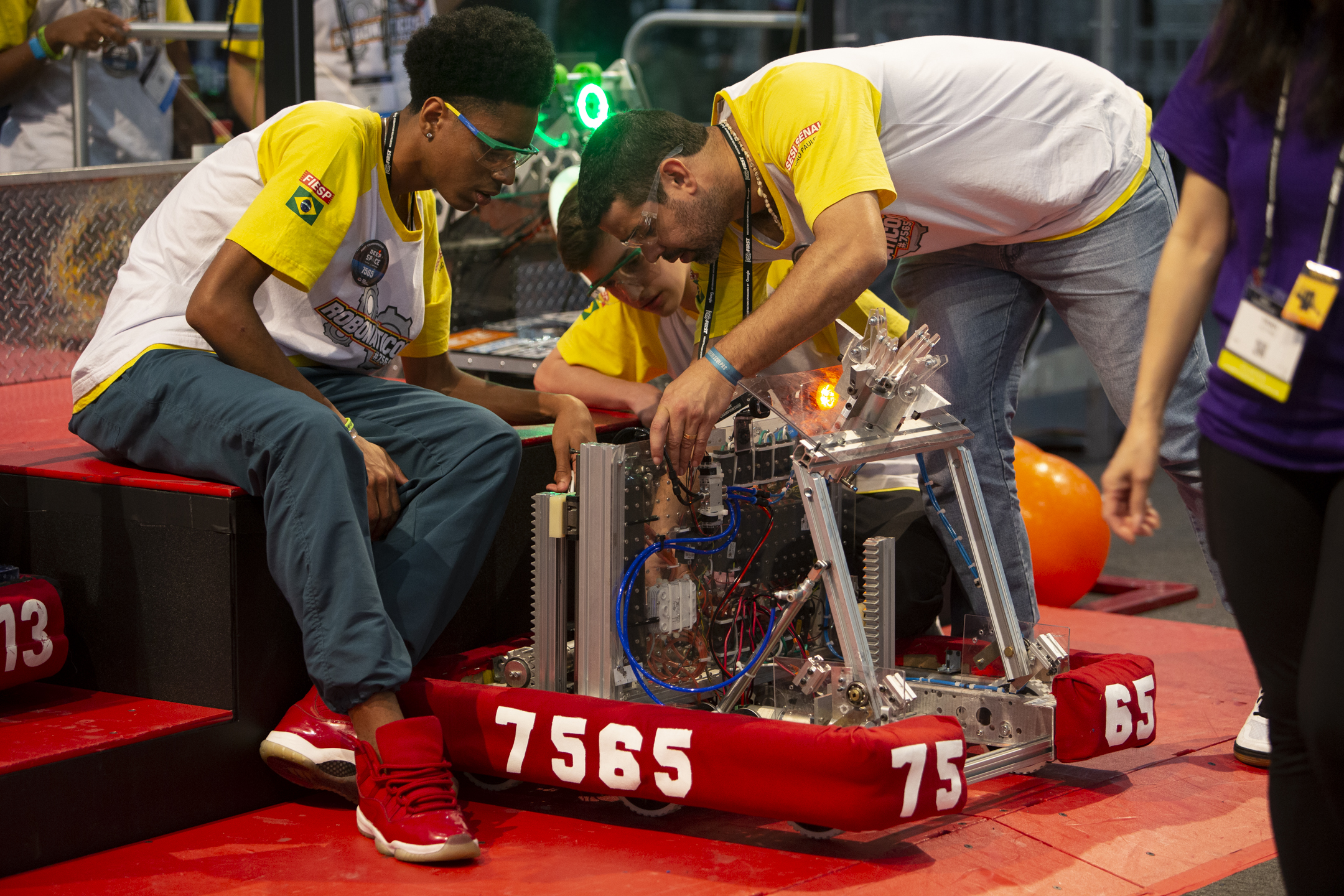
Robotics Competition partners (like FIRST and RECF) design challenges require students to design, build and troubleshoot industrial level robots under the guidance of industry mentors. The high school level robots are not built from a kit but are designed based on specifications that change every year. The project provides students with opportunities to develop technical skills like designing wiring harnesses, integrating sensing systems, designing end effectors, power distribution systems, and control systems.
This level of electromechanical design and debugging exposes students to the type of competencies and skills that ARM member industries would like to see in their technicians. SMART works with industry partners to develop ARM industry-recognized assessments that students complete as they engage in competition activities.
ARM members have committed to work collaboratively with SMART to design the assessments that upon completion will enable students to earn M-Cs that eventually lead to a certification.
Why Robotics Competitions?
High school robotics competition (e.g. FIRST, RECF) programs require students to design, build and troubleshoot industrial level robots under the guidance of industry mentors. The high school level robots are not built from a kit but are designed based on specifications that change every year. Students are required to design wiring harnesses, integrate sensing systems, design end effectors, power distribution systems, and control systems. This level of electromechanical design and debugging exposes students to the type of competencies and skills that ARM member industries would like to see in their technicians. SMART works with industry partners to develop ARM industry-recognized assessments that students complete as they engage in robotics competition activities. ARM members have committed to work collaboratively with SMART to design the assessments that upon completion will enable students to earn M-Cs that eventually lead to a certification.
Why Carnegie Mellon Robotics Academy?
The Robotics Academy has supported the robotics competition community since 2000. The Robotics Academy's mission is to use the motivational effects of robotics to excite students about CS-STEM education. Our curriculum has been adopted in over 16,000 schools, and the instructional technologies are used by over 1 million students every day. The Robotics Academy has developed curricula for LEGO and VEX Robot kits since 2004 and the curricula are posted online for free for schools to use. in 2013, we began developing curricula for the Arduino microcontroller for advanced high school programs. The SMART Project builds on those lessons and leverages the Computer Science STEM Network to measure student learning. Initially, the project reaches students and teachers through Robotics Academy and FIRST established networks, but, SMART project developers expect ARM member companies and educational partner network to adopt the M-C pathway model based on its effectiveness at foregrounding ARM competencies and addressing regional ARM outreach and talent development. The new project leverages the inexpensive Raspberry Pi to teach integration and debugging skills.
SMART training materials use inexpensive technologies such as the Arduino Uno, a mini-computer to which a plethora of sensors and peripherals can be attached. It operates on a Linux Operating System, which is widely used in robotics, making it an ideal platform for training technicians. Courses will teach systems integration and debugging skills.