Digital Evidence Vault: An evidence vault for open source investigations
What is Digital Evidence Vault?
The volume of information available to human rights practitioners has steadily grown with the globalization of Internet access and the widespread adoption of smartphones across geographies, cultures, and socioeconomic classes. This vast digital landscape creates an unprecedented audiovisual record of the experiences of a significant percentage of humanity. It also provides human rights practitioners and organizations with access to information about issues, events, and locations that were previously inaccessible to them.
When properly collected and analyzed, this material can help human rights analysts, fact-finders, and researchers reconstruct events of interest, including war crimes, human rights violations, and terrorist acts. At the same time, the availability of massive volumes of multiformat media has created new technical challenges for the human rights community that require solutions that are not currently commercially available.
The Center for Human Rights Science created Digital Evidence Vault (DEV) to solve one of these problems: the need to quickly and efficiently collect and preserve this content in a way that ensures its future accessibility and evidentiary value.
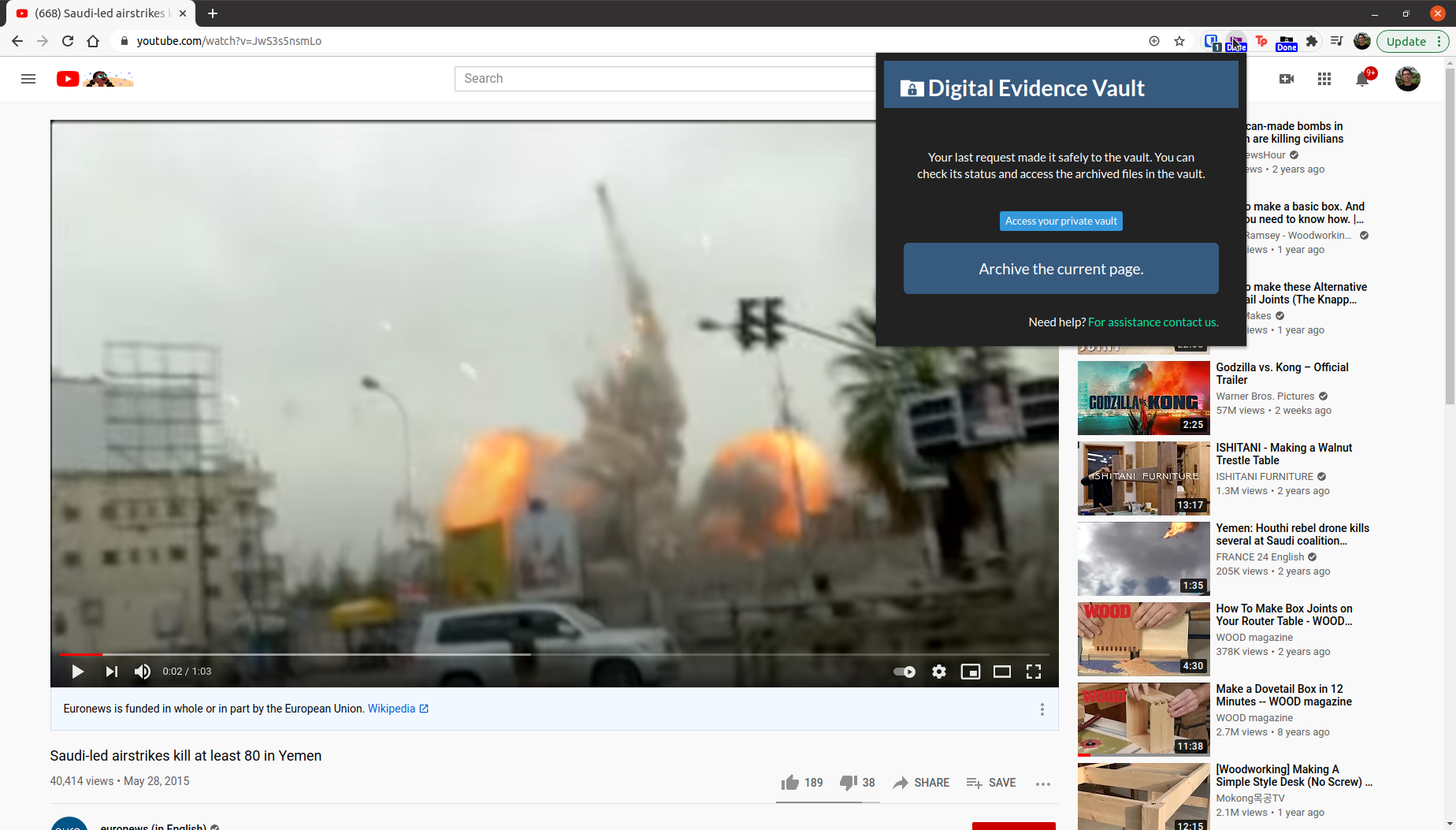
DEV makes it possible to collect and preserve HTML, video, audio, and associated metadata at the click of a button from thousands of sources, including YouTube, Facebook, Twitter, LiveLeak, and virtually any other service that exists on the Internet.
DEV ensures that this digital material will be available for transparency and accountability efforts, criminal tribunals, and historical clarification. It has been built to ensure the credibility and admissibility of this material in both national courts and international tribunals. It has been used by hundreds of researchers, and dozens of organizations and institutions, around the world since it was developed in 2013.
How Does Digital Evidence Vault work?
Digital Evidence Vault provides a simple and usable way to submit digital assets available online to an engine that performs the automated collection of the available digital assets.
The system can be accessed by individuals and organizations as a public service at or can be installed as a private instance for an organization, with customizations according to their workflow including tools for collaboration, collection management, sharing, backup, and analysis.
The engine relies on a number of microservices that perform specific tasks that follow best practices to enhance the evidentiary weight.
Automated collection
It allows for the automated collection of publically available URLs, as well as content that requires login credentials like Facebook groups or Telegram channels.
The collection includes:
- A screenshot of the full page
- Video and/or audio files for URLs that point to pages that contain it as a primary asset, like YouTube and Vimeo videos or Tweets and Facebook posts with video.
- Publically available metadata
- The rendered HTML as a file
- Thumbnails, when available.
- Information on the time of the request, start and end time of collection, IP associated with the target URL, IP of the requester, account id of the requester and other
Chain of custody and trusted timestamping
- Each individual file is hashed using MD5 or SHA-256 (depending on the needs of the collection teams)
- All files are packaged in a zip file that includes a digest of files and hashes. The file is then hashed using SHA-256 and later submitted to a third-party Trusted Timestamping service to enhance the ability to verify that any given content was collected and existed at a given time.
Analysis and reporting
- Printable report of the individual evidence collection packages containing all request and collection information such as
- Requester
- Date and time of the request
- Original provider
- Original URL
- Start and end collection time
- Captured site IP
- Requester IP
- Preservation package file name and file size
- Package SHA256 hash
- Digital Evidence Vault version number
- Digest of files in the folder with the corresponding MD5 hash
- Evidence package review page that allows for the review of videos, including tools for zoom-in and out, frame extraction, and playback speed control. It also allows exporting a package or a single frame to Dropbox. The review page automatically extracts keyframes from the video and displays them to simplify the review of video material. It also uses WebRTC to facilitate in-page video calls for teams to review collaboratively material.
Digital Evidence vault provides various methods for the submission of URLs:
- API: a RESTful API that allows for the programmatic submission of URLs, the retrieval of information on the status of a request, and the listing of assets associated with an account.
- Web interface: a publicly available interface that allows for the submission of a request for collection. The results are sent back to the user over email where the user can access a URL to the collection report as well as the collected assets.
- Browser extension: Digital Evidence Vault provides a simple way to submit URLs directly from the browser and that facilitates the review of the status of a request as well as the access to previously requested content.
- Bulk import: On request, users can submit spreadsheets or similar files containing multiple URLs. The URLs are processed in bulk and the resulting collection packages are added to their account.
Upcoming features
- Assistance in deduplication and verification
- Zero knowledge repository for secure information sharing across organizations
- Collection of materials in the dark web