Electrified Vehicles
The term "electrified vehicles" refers to a range of technologies that use electricity to propel a vehicle:
- HEV: Hybrid Electric Vehicles obtain all net propultion energy from petroleum but use an electrical system to improve fuel efficiency.
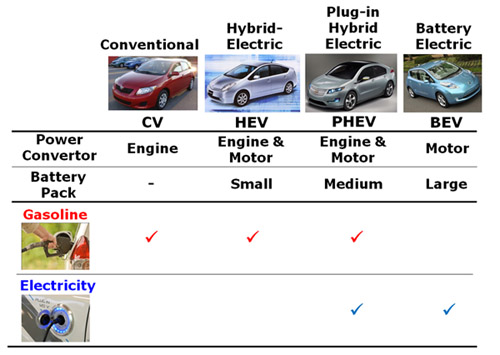
- PHEV: Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles store energy from the electric power grid and can drive partly using electricity and partly using petroleum. There are two main variants:
- Blended PHEVs use a mix of gasoline and electricity when the battery is charged and then switch entirely to gasoline when the battery is depleted. An advantage to blended operation is that because the electrical system does not need to satisfy peak power demands on its own, it can be smaller.
- Extended Range Electric Vehicles (EREVs) are PHEVs that use only electricity when the battery is charged and switch to gasoline when the battery is discharged. For trips shorter than the range of the battery, the vehicle operates as a BEV.
- BEV: Battery Electric Vehicles have larger battery packs to store more energy from the electric power grid for longer range. They have no backup gasoline engine. BEVs are also referred to by some as "pure-electric vehicles" or "all-electric vehicles" (AEVs).
- FCEV: Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles refuel with hydrogen and use a fuel cell to produce electricity to propel the vehicle. FCEVs are also referred to as fuel cell vehicles or FCVs.

Other terms:
- PEV: Plug-in Electric Vehicle is a term used to refer to all vehicles that plug in to charge from the electric power grid (BEVs and PHEVs).
- EV: Electric Vehicle is a term that is used inconsistently. Some use the term EV to refer to BEVs specifically, while others use EV to refer to PEVs, PEVs + FCEVs, or even any electrified vehicle.
List of plug-in vehicles available or planned for commercialization
List of U.S. laws and incentives related to electrified vehicles